Abstract
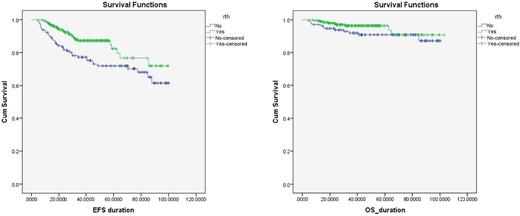
Background & aim of the study: The major challenge in advanced stage Hodgkin Lymphoma is to optimize the balance between overall survival and treatment related toxicity. The aim of the study was to describe the pediatric population with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) in our country receiving Involved Field Radiotherapy (IFR) and their treatment outcome compared to those who did not.Patients and methods: This is a retrospective single center study. Data analysis for children with advanced stage HL (IIB or IIIB with bulk disease, or stage IV) as done. Demographic data, staging, number of cycles (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine (ABVD)) received and whether or not consolidation radiotherapy (RTH) was administered. Positron emission tomography (PET) was performed baseline and after the second cycle to detect early response without any change to treatment plan. Results: Three hundred and eighty-one patients with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma were enrolled in the data analysis. Male (283) to female (98) ratio 3:1. B-symptoms was present in 60% of patients. Ann Arbor staging distribution was as follows; 68 (17.8%) IIB, 97 (25.5%) IIIA, 96 (25.2%) IIIB, 55 (14.4%) IVA, 65 (17.1%) IVB. One hundred sixty-five patients with early unfavorable and 216 with advanced-stage disease were treated with ABVD ± RTH. One hundred twenty- nine (34%) patient did not receive RTH. The Five-years Overall survival (OS) and the Event free survival (EFS) in these patients was 90.7 (95% CI: 85.4-95.9 and 71.9% (95% CI: 63.6-76.1) (p value 0.006) respectively. The OS and EFS of patient with advanced stage HL in the whole study population was 94.1 (95% CI: 91.5-96.6) and 79.4 (95% CI 74.3-84.4) respectively. Conclusion: More than 90% of patients are cured with risk-based combined-modality therapy, yet these therapies are frequently associated with risks for significant long term toxicities; innovative approaches are needed for those patients who have a high risk of failure with current therapies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal